-
Decorator Pattern(데코레이터 패턴)STUDY/디자인패턴 2024. 12. 25. 15:57
데코레이터 패턴이란?
객체들을 새로운 행동들을 포함한 특수 래퍼 객체들 내에 넣어서 위 행동들을 해당 객체들에 연결시키는 구조 패턴으로, 상속을 통해 클래스를 확장하는 대신, 객체를 감싸는 방식을 사용하여 기능을 추가하거나 변경한다.
구조
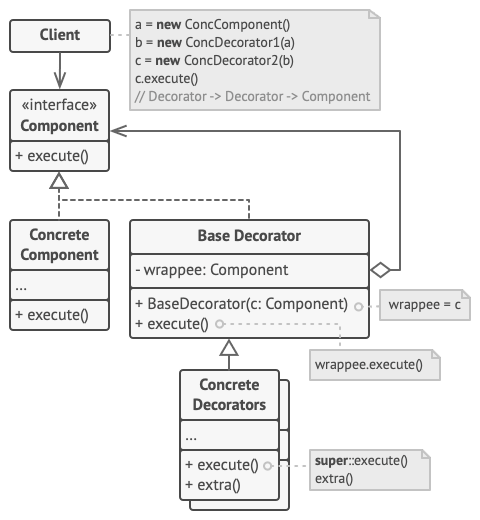
- Component
래퍼들과 래핑된 객체들 모두에 대한 공통 인터페이스를 선언
- Concrete Component
래핑되는 객체들의 클래스이며, 기본 행동들을 정의하고 해당 기본 행동들은 데코레이터들이 변경할 수 있다.
- Base Decorator
래핑된 객체를 참조하기 위한 필드가 있고, 필드의 유형은 구상 컴포넌트들과 구상 데코레이터들을 모두 포함할 수 있도록 컴포넌트 인터페이스로 선언되어야 한다. 그 후 기초 데코레이터는 모든 작업들을 래핑된 객체에 위임한다.
- Concrete Decorators
컴포넌트들에 동적으로 추가될 수 있는 추가 행동들을 정의한다. 기초 데코레이터의 메서드를 오버라이드(재정의)하고 해당 행동을 부모 메서드를 호출하기 전이나 후에 실행한다.
- Client
데코레이터들이 컴포넌트 인터페이스를 통해 모든 객체와 작동하는 한 컴포넌트들을 여러 계층의 데코레이터들로 래핑할 수 있다.
예시
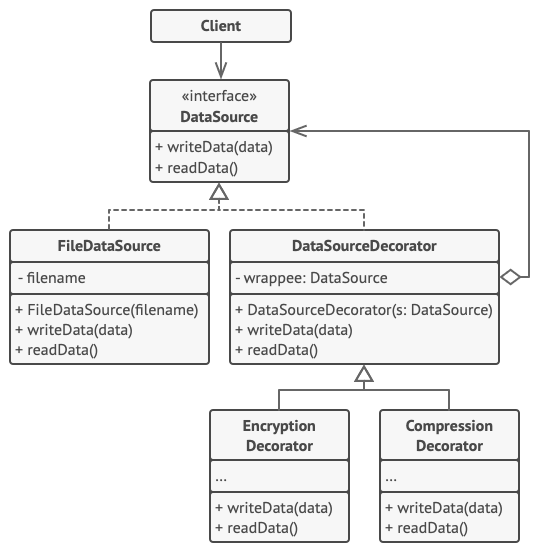
Component
public interface DataSource { void writeData(String data); String readData(); }Concrete Component
public class FileDataSource implements DataSource { private String name; public FileDataSource(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void writeData(String data) { File file = new File(name); try (OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file)) { fos.write(data.getBytes(), 0, data.length()); } catch (IOException ex) { System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); } } @Override public String readData() { char[] buffer = null; File file = new File(name); try (FileReader reader = new FileReader(file)) { buffer = new char[(int) file.length()]; reader.read(buffer); } catch (IOException ex) { System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); } return new String(buffer); } }Base Decorator
public abstract class DataSourceDecorator implements DataSource { private DataSource wrappee; DataSourceDecorator(DataSource source) { this.wrappee = source; } @Override public void writeData(String data) { wrappee.writeData(data); } @Override public String readData() { return wrappee.readData(); } }Concrete Decorators
public class EncryptionDecorator extends DataSourceDecorator { public EncryptionDecorator(DataSource source) { super(source); } @Override public void writeData(String data) { super.writeData(encode(data)); } @Override public String readData() { return decode(super.readData()); } private String encode(String data) { byte[] result = data.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) { result[i] += (byte) 1; } return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(result); } private String decode(String data) { byte[] result = Base64.getDecoder().decode(data); for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) { result[i] -= (byte) 1; } return new String(result); } } public class CompressionDecorator extends DataSourceDecorator { private int compLevel = 6; public CompressionDecorator(DataSource source) { super(source); } public int getCompressionLevel() { return compLevel; } public void setCompressionLevel(int value) { compLevel = value; } @Override public void writeData(String data) { super.writeData(compress(data)); } @Override public String readData() { return decompress(super.readData()); } private String compress(String stringData) { byte[] data = stringData.getBytes(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream(512); DeflaterOutputStream dos = new DeflaterOutputStream(bout, new Deflater(compLevel)); dos.write(data); dos.close(); bout.close(); return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(bout.toByteArray()); } catch (IOException ex) { return null; } } private String decompress(String stringData) { byte[] data = Base64.getDecoder().decode(stringData); try { InputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(data); InflaterInputStream iin = new InflaterInputStream(in); ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream(512); int b; while ((b = iin.read()) != -1) { bout.write(b); } in.close(); iin.close(); bout.close(); return new String(bout.toByteArray()); } catch (IOException ex) { return null; } } }Client
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { String salaryRecords = "Name,Salary\nJohn Smith,100000\nSteven Jobs,912000"; DataSource dataSource = new FileDataSource("out/Output.txt"); DataSourceDecorator encoded = new EncryptionDecorator(dataSource); encoded.writeData(salaryRecords); System.out.println(dataSource.readData()); System.out.println(encoded.readData()); DataSourceDecorator compression = new CompressionDecorator(dataSource); compression.writeData(salaryRecords); System.out.println(dataSource.readData()); System.out.println(compression.readData()); } } # 결과 T2JuZi1UYm1ic3oLS3BpbyFUbmp1aS0yMTExMTELVHVmd2ZvIUtwY3QtOjIzMTEx Name,Salary John Smith,100000 Steven Jobs,912000 eJzzS8xN1QlOzEksquTyys/IUwjOzSzJ0DE0AAGu4JLUstQ8Ba/8pGIdS0MjoBAAfpEOqg== Name,Salary John Smith,100000 Steven Jobs,912000패턴적용
- 객체를 사용하는 코드를 손상시키지 않고 런타임에 객체에 추가 동작을 할당할 수 있어야 하는 경우
- 상속을 사용하여 객체의 행동을 확장하는 것이 어색하거나 불가능한 경우
장단점
장점
- 새 자식 클래스를 만들지 않고도 객체의 행동을 확장할 수 있다.
- 런타임에 객체들에서부터 책임들을 추가하거나 제거할 수 있다.
- 객체를 여러 데코레이터로 래핑하여 여러 행동들을 합성할 수 있다.
- 단일 책임 원칙 : 다양한 행동들의 여러 변형들을 구현하는 모놀리식 클래스를 여러 개의 작은 클래스들로 나눌 수 있다.
단점
- 래퍼들의 스택에서 특정 래퍼를 제거하기 어렵다.
- 어느 테코레이터를 먼저 설정하느냐에 따라 스택 순서가 결정되기 때문에, 데코레이터 스택 내의 순서에 의존하지 않는 방식으로 데코레이터를 구현하기 어렵다.
- 계층들의 초기 설정 코드가 보기 안좋을 수 있다.(ex. new A(new B(new C(new D()))))
'STUDY > 디자인패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
Composite Pattern(복합체 패턴) (0) 2024.12.25 Bridge Pattern(브리지 패턴) (0) 2024.12.08 Adapter Pattern(어댑터 패턴) (0) 2024.12.08 Singleton Pattern(싱글턴 패턴) (0) 2024.11.26 Prototype Pattern(프로토타입 패턴) (0) 2024.11.26