-
Template Method Pattern(템플릿 메서드 패턴)STUDY/디자인패턴 2025. 3. 3. 19:06
템플릿 메서드 패턴이란?
부모 클래스에서 알고리즘의 골격을 정의하지만, 해당 알고리즘의 구조를 변경하지 않고 자식 클래스들이 알고리즘의 특정 단계들을 재정의할 수 있도록 하는 행동 디자인 패턴
템플릿 메서드 패턴은 알고리즘을 일련의 단계들로 나누고, 이러한 단계들을 메서드들로 변환한 뒤, 단일 템플릿 메서드 내부에서 이러한 메서드들을 호출한다.
이러한 단계들은 abstract(추상)이거나 일부 디폴트 구현을 가지게 된다. 알고리즘을 사용하기 위해 클라이언트는 자신의 자식 클래스를 제공해야 하고, 모든 추상 단계를 구현해야 하며, 필요하다면 (템플릿 메서드를 제외한) 선택적 단계 중 일부를 오버라이드(재정의)해야 한다.
- 모든 자식 클래스는 추상 단계들을 구현해야 한다.
- 선택적 단계들에는 이미 어떤 디폴트(기본값) 구현이 있지만, 필요한 경우 이를 무시하고 오버라이드(재정의) 할 수 있다.
- '훅'은 몸체가 비어 있는 선택적 단계로, 해당 단계는 오버라이드 되지 않아도 작동한다.
구조
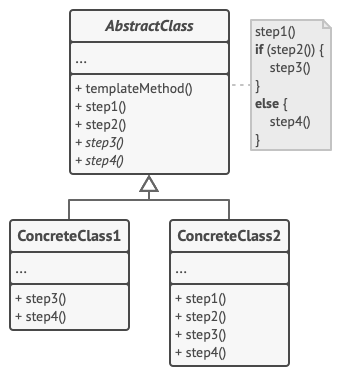
- AbstractClass
추상 클래스는 알고리즘의 단계들의 역할을 하는 메서드들을 선언하며, 이러한 메서드를 특정 순서로 호출하는 실제 템플릿 메서드도 선언한다. 단계들은 abstract로 선언되거나 일부 디폴트 구현을 갖는다.
- ConcreteClass
구상 클래스들은 모든 단계들을 오버라이드할 수 있지만 템플릿 메서드 자체는 오버라이드 할 수 없다.
예시
AbstractClass
public abstract class Network { String userName; String password; Network() {} public boolean post(String message) { if (logIn(this.userName, this.password)) { boolean result = sendData(message.getBytes()); logOut(); return result; } return false; } abstract boolean logIn(String userName, String password); abstract boolean sendData(byte[] data); abstract void logOut(); }ConcreteClass1
public class Facebook extends Network { public Facebook(String userName, String password) { this.userName = userName; this.password = password; } public boolean logIn(String userName, String password) { System.out.println("\nChecking user's parameters"); System.out.println("Name: " + this.userName); System.out.print("Password: "); for (int i = 0; i < this.password.length(); i++) { System.out.print("*"); } simulateNetworkLatency(); System.out.println("\n\nLogIn success on Facebook"); return true; } public boolean sendData(byte[] data) { boolean messagePosted = true; if (messagePosted) { System.out.println("Message: '" + new String(data) + "' was posted on Facebook"); return true; } else { return false; } } public void logOut() { System.out.println("User: '" + userName + "' was logged out from Facebook"); } private void simulateNetworkLatency() { try { int i = 0; System.out.println(); while (i < 10) { System.out.print("."); Thread.sleep(500); i++; } } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } }ConcreteClass2
public class Twitter extends Network { public Twitter(String userName, String password) { this.userName = userName; this.password = password; } public boolean logIn(String userName, String password) { System.out.println("\nChecking user's parameters"); System.out.println("Name: " + this.userName); System.out.print("Password: "); for (int i = 0; i < this.password.length(); i++) { System.out.print("*"); } simulateNetworkLatency(); System.out.println("\n\nLogIn success on Twitter"); return true; } public boolean sendData(byte[] data) { boolean messagePosted = true; if (messagePosted) { System.out.println("Message: '" + new String(data) + "' was posted on Twitter"); return true; } else { return false; } } public void logOut() { System.out.println("User: '" + userName + "' was logged out from Twitter"); } private void simulateNetworkLatency() { try { int i = 0; System.out.println(); while (i < 10) { System.out.print("."); Thread.sleep(500); i++; } } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } }적용
- 클라이언트들이 알고리즘의 특정 단계들만 확장할 수 있도록 하고, 전체 알고리즘이나 알고리즘 구조는 확장하지 못하도록 하는 경우
- 약간의 차이는 있지만 거의 같은 알고리즘들을 포함하는 여러 클래스가 있는 경우
장단점
장점
- 클라이언트들이 대규모 알고리즘의 특정 부분만 오버라이드하도록 하여 그들이 알고리즘의 다른 부분에 발생하는 변경에 영향을 덜 받도록 할 수 있다.
- 중복 코드를 부모 클래스로 가져올 수 있다.
단점
- 일부 클라이언트들은 알고리즘의 제공된 골격에 의해 제한될 수 있다.
- 자식 클래스를 통해 디폴트 단계 구현을 억제하여 리스코프 치환 원칙을 위반할 수 있다.
- 템플릿 메서드들은 단계들이 더 많을수록 유지가 더 어려운 경향이 있다.
'STUDY > 디자인패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
Visitor Pattern(방문자 패턴) (0) 2025.03.03 Strategy Pattern(전략 패턴) (0) 2025.03.03 State Pattern(상태 패턴) (0) 2025.02.16 Observer Pattern(옵저버 패턴) (0) 2025.02.16 Memento Pattern(메멘토 패턴) (0) 2025.02.16